Country Overview
Georgia is a Post-Soviet country, located right between Asia and Europe on a historical “Silk Road”, connecting two continents and offering the best of both to its visitors. Since 2003’s “Rose Revolution” the Government and the Economics of Georgia have drastically changed and shifted to the better by implementing reforms for liberalization, provision of feasible growth of Georgian Economy and fight towards corruption.
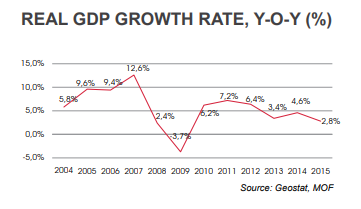
Due to those reforms Georgia has been exceptionally resilient to outside shocks, such as global financial crisis and such and has been recognized as a leader in fighting corruption by the World Bank in 2012. Over the last few years Georgia has had one of the fastest growing economy in Europe and reached its highest level of GDP in 2007 with average of 12.3%, making the overall expansion of its economy 35%.
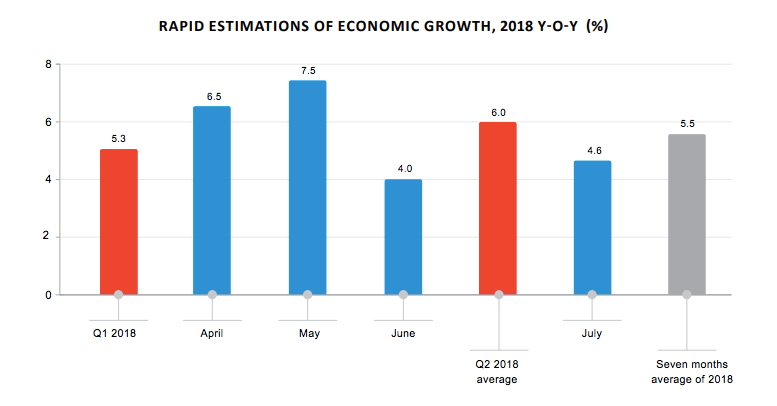
The estimated real GDP growth rate in July 2018 amounted to 4.6% y-o-y according to National Statistics Office of Georgia. An average estimated real GDP growth equaled 5.5% for the first seven months of 2018 y-o-y. In July 2018 the estimated real growth, compared to the same period of the previous year, was in transportation, trading areas, real estate, financial intermediation, hotels and restaurants.
Business Environment
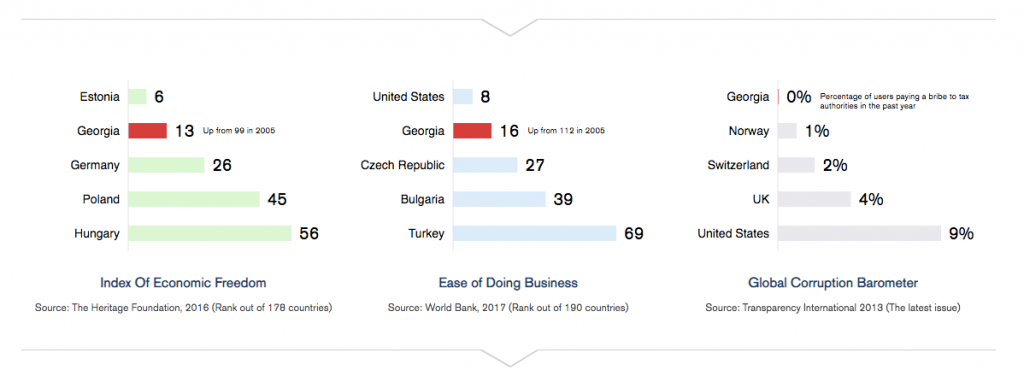
Georgia has a very stable political environment, efficient, pro-business and corruption-free government, liberal and free market economy, low tax system, competitive cost of labor and energy, developed transport infrastructure, large size of market by Free Trade Agreements and after signing the Association Agreement on 27th June 2014 between Georgia and EU, the country gradually integrates it’s economy with the European economy. Georgia is now considered as one of the best countries in the world in easy of doing business. It’s ranked ninth globally in the World Bank Group’s Doing Business 2018 among 190 economies. And it’s 16th most secured country in the world according to Global Competitiveness Index -2015/2016.
According to “Best European Countries for Business 2018” the rating list of European Chamber, Georgia took 18th place out of 46. European Chamber rates countries depending on their business environment. The rating scores depend on World Bank business making index and transparent corruption index rating. Number one in rating is Denmark with 87 points. Georgia has 62 points. The last in the rating is Ukraine. In 2017 Georgia was in 20th place.
Georgia ranks 16th among 186 countries in the Heritage Foundation 2018 Index of Economic Freedom. The Heritage Foundation’s Economic Freedom index rates countries on ten economic freedom factors. The maximum possible score for each factor is 100. Georgia received its highest score in fiscal health with 91.8 and trade freedom with 89.4%. After the 2003 “Rose Revolution,” several reforms by successive administrations have reduced petty corruption, cut regulation, simplified taxes, opened markets and developed transport and energy infrastructure. Resulting in improvement in the state of country’s economy and its economic freedom growth.
Investment Environment
Over the past decade Georgia committed efforts to increase investments. The government has reformed the tax system, made customs procedures simpler, easier and more efficient, under the IFC Georgia Investment Climate Project with the help of World Bank Group has developed more investor-friendly policies.
According to Jan vas Bilsen, IFC Regional Manager for the South Caucasus, “Georgia’s impressive progress in improving its business climate has been well reflected in international rankings. However, investors also consider a country’s investor protection guarantees and their implementation, so we have worked with the government in these areas to help Georgia achieve its long-term development objectives”.
Georgia has signed FTAs with CIS countries that include Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan, as well as its neighbors, Turkey, Azerbaijan and Armenia. After signing EU-Georgia Association Agreement, the EU and Georgia have also entered into a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area (DCFTA). In January-May 2018, trade turnover with European Union (EU) countries increased by 23% year-on-year (y/y) and amounted to $1.34 billion, shows the data from the National Statistics Office of Georgia. Exports were worth $295.7 million (13.7% higher), while imports reached $1.04 billion (25.9% higher). The EU is Georgia’s largest trading partner and provides over €100 million to Georgia annually in technical and financial assistance.
Taxation
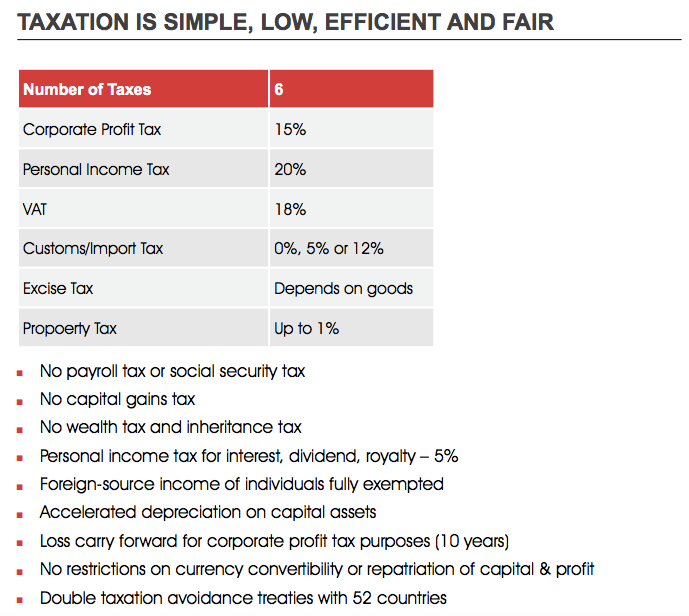
Georgia has one of the most liberal entrepreneurial legislations. For the past decade Georgian economy has demonstrated a high level of resilience. The overall freedom to conduct business is relatively well protected in Georgia’s regulatory environment. For example, starting a business takes an average of 2 days, compared to the world average of 20 days.
Energy Sector
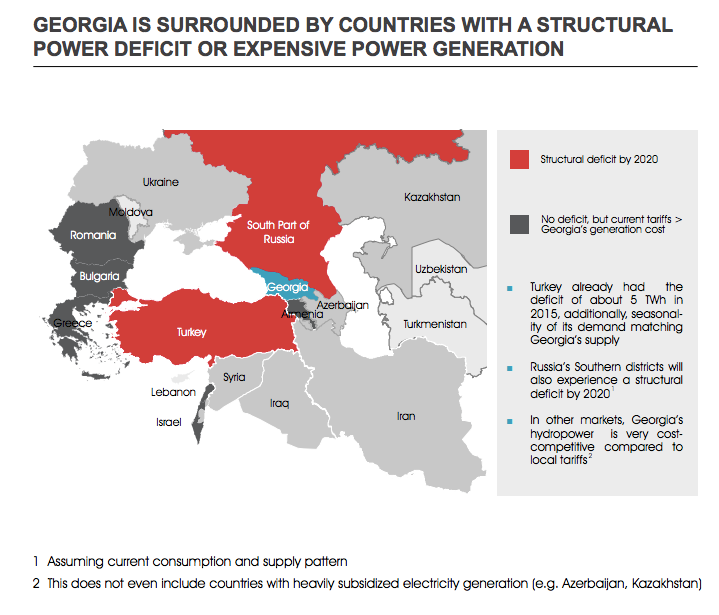
Georgia has investment opportunities in different fields. In energy sector Georgia has huge untapped potential and strong demand growth prospects. 75% of economically viable hydropower potential is not yet exploited. Georgia is one of the top countries in terms of water resources per Capita. Over 60 potential HPP projects on the Pre-feasibility Study Level with Financial and Technical projection are available for investors. In addition to hydro, there is considerable generation potential from wind, solar and other renewable sources. It’s also important fact that Georgia is surrounded by countries with a structural power deficit or expensive power generation.
Hospitality & Real Estate Sectors
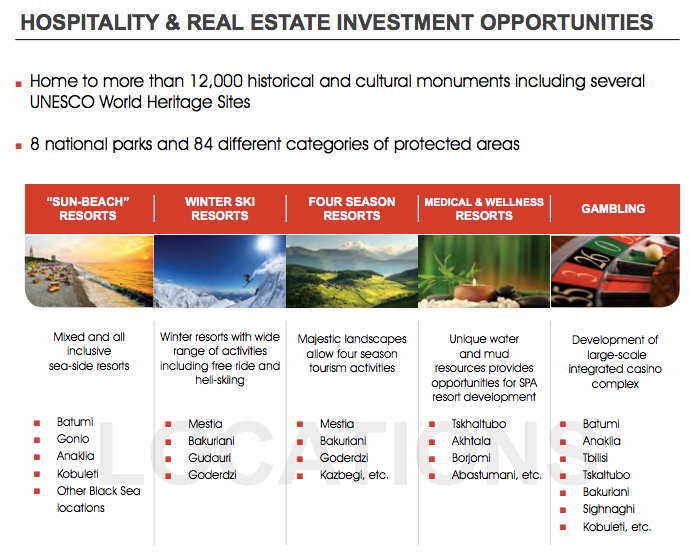
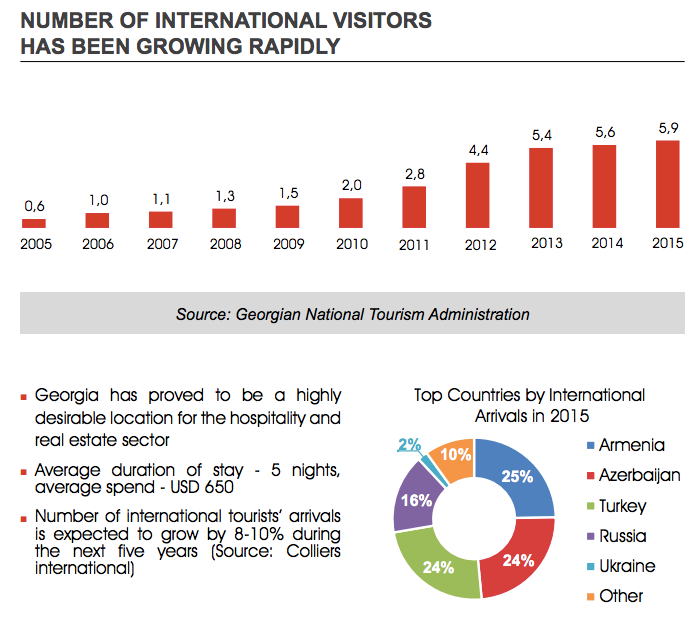
Another field is hospitality and real estate sector. Georgia has 23% average annual growth of international visitors for last five years. Its unique nature and culture and various types of resorts are very attractive investment opportunities for lots of investors.
According to the Georgian National Tourism Administration in January – April 2018 the number of international arrivals in Georgia amounted to 2,060,264, showing an increase of 15.9% compared to the same period of previous year. The majority of foreign travelers were Azerbaijanian (-0.5%), Armenian (+8.7%), Turkish (+23.9%), Russian (+31.2%) and Iranian (+69.3%).
A positive trend in arrivals was also observed among citizens of the European Union countries. A notable increase was registered of Estonian +83.1%, Latvian +55.8%, British +46.6%, Spanish +43.9%, Dutch +38.4% and French +24.4% travelers. Exceptional growth in arrivals was recorded of citizens of the following countries: Kuwait +111.4%, Iran +69.3%, China +58.2%, Saudi Arabia +57.9% and Israel +49.7%.
Georgia has no real estate ownership restrictions. The country has Visa Free Regime with 94 countries and that’s the result of governmental incentives in this sector. Georgia is 16th most secured country in the world according to Global Competitiveness Index -2015/2016.
Manufacturing Sector
Georgia’s current advantages in terms of handling large transshipment flows, business stability, low cost of power generation, existing raw materials and intermediate products provide opportunities for large industrial projects, such as production of iron, aluminum and steel products.
Georgia has growing regional market and access to 900 million markets without Customs Duty (FTA, DCFTA), competitive labor costs – the average monthly salary in manufacturing industry was 355 USD (2015) including white and blue-collar workers, and low utility and energy costs, 4 Free Industrial Zones (FIZ) – in FIZ businesses are exempt from all taxes except Personal Income Tax (20%), which is paid from employees’ salaries.
Agriculture
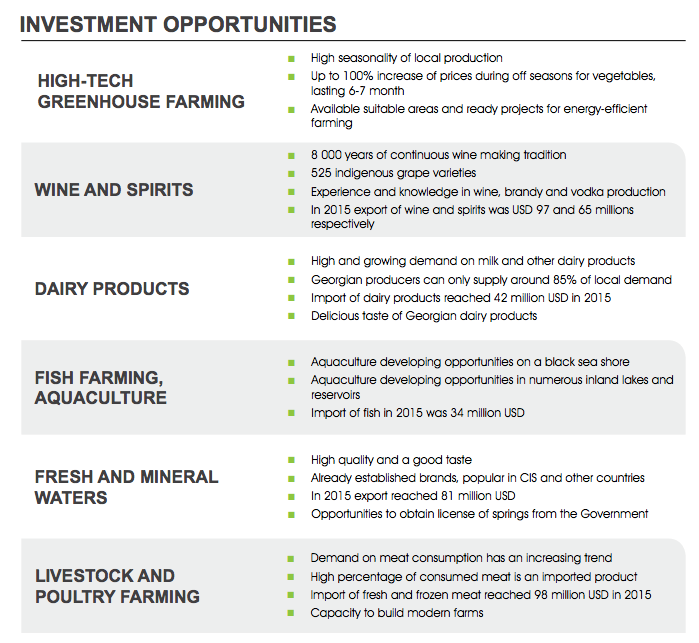
Beside the advantages of market size, Georgia has ecological clean environment, 22 microclimates varying from cool and dry to warm and humid, longer than normal harvesting season and a wide range of growing conditions, large quantity of renewable water, pure, rich and pesticide-free soil, cheap labor and low utility costs. More importantly agricultural sector has as financial and technical, as well as infrastructural support from the government. It’s also important fact that there is rapidly growing local and regional demand and strong preference of consumers toward Georgian products.
Logistics Sector
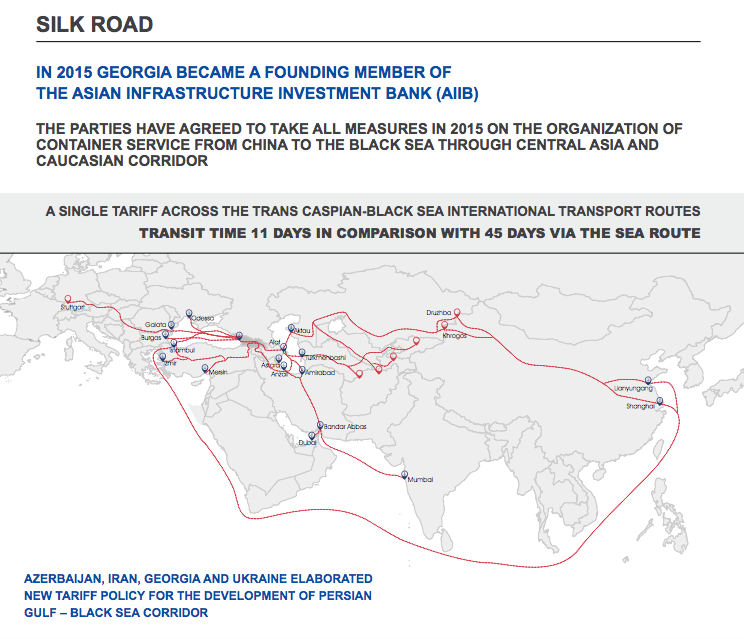
Georgia is an attractive gateway between Europe and Central Asia. Trans-Caucasian Route is one of the most important for the country. FDI inflows in the transport and communication sector have primarily targeted transport infrastructure. Ports are cost competitive and alternative routes as well and the government is rapidly developing road infrastructures.
Baku-Tbilisi-Kars project has also crucial importance for the country, as it’s direct connection with European and Central Asian railway networks. BTK project was inaugurated in the ceremony on 30th October 2017 and is intended to complete a transport corridor linking Azerbaijan to Turkey (and therefore Central Asia and China to Europe) by rail. Trade between China and Turkey amounted to USD 27 billion in 2015 and it is expected to triple by the 2020. The line is intended to transport an initial annual volume of 6.5 million tones, rising to a long-term target of 17 million tones.
There is also one major ongoing project, development of deep-sea port in Anaklia, which has a 18-20 m natural draft and possibility to receive the fifth-generation vessels such as Panamax and has full support from the government. Port will be focused on containers and bulk/mixed cargoes.